Tick-Borne Illnesses
Tick-Borne Illnesses
TICK-BORNE ILLNESSES
INSTRUCTOR: Brigitta Jansen, MS, CNS, CDN
FALL 2025. FRIDAYS AT 3PM
SYLLABUS (Subject to change)
Dive into the intricate world of tick-borne illnesses with our comprehensive course, designed to unravel the complexities of diseases transmitted by ticks, their profound impact on human health, and the forefront of prevention and treatment strategies. This course offers a deep dive into the biology of ticks, the pathogens they carry, and the myriad ways these diseases affect the human body, from acute infections to chronic conditions and autoimmune responses. Through detailed lectures ranging from the transmission vectors and biological foundations of tick-borne pathogens to the clinical manifestations, diagnosis, and management of diseases like Lyme Borreliosis, students will gain a holistic understanding of the challenges and controversies surrounding these conditions. The course not only covers the pharmacological and alternative therapies currently in use but also explores the nutritional implications and future challenges in the field. Designed for healthcare professionals, researchers, and anyone keen to understand the nexus of ecology, microbiology, and clinical medicine, this course equips participants with the knowledge to contribute to the evolving battle against tick-borne diseases, emphasizing a multidisciplinary approach and patient-centered care.
UNIT 1: Introduction & Overview
Lecture 1: Course Overview and Importance of Studying Tick-borne Diseases
- Class Notes:
- Introduction to Lyme Borreliosis & Co-infections
- Incidence in Populations
- Myths about Lyme disease
- History of Lyme disease
- Socio-economic and health impact of acute and chronic Lyme.
____
UNIT 2: Biological Foundations
Lecture 2: Transmission Vectors
- Class Notes:
- Morphology and anatomy of ticks.
- Life stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult.
- Feeding habits and host preferences.
- Other Vectors and transmission routes for Lyme & Co
- Mechanisms of Pathogen Transmission
- Tick feeding mechanism and how it facilitates transmission.
- Tick salivary glands and their role in pathogen transmission.
- Factors influencing transmission rates.
- Environmental factors favoring tick proliferation.
- Geographic distribution of major tick species.
- Climate change and tick migration.
- Principles of host-vector-pathogen interactions.
- Evolutionary pressures and adaptation mechanisms.
- Impact of host biodiversity on tick-borne disease risk.
Lecture 3: Tick-borne Pathogens
- Class Notes:
- Introduction to bacteria, viruses, and protozoa carried by ticks.
- Common tick-transmitted pathogens like Borrelia, Anaplasma, Mycoplasma, Rickettsia,
Spotted Mountain Fever and Babesia
- Associations with chronic diseases
Lecture 4: Biology of Spirochetes
- Class Notes:
- Taxonomy
- Anatomy & method of motility
- Genomics & Plasmids
- Reproduction and transmission aspects
- Spirochetes in human tissues
- Intracellular persistence and migration
- Persistence in Biofilm
- Connection to Parasites
Lecture 5: Testing for Tick-borne Diseases
- Class Notes:
- Diagnostic methods and challenges
- Antibody testing: IgG, IgM
- PCR, T-cell Activation Test
- Immune aspects affecting testing.
- Sensitivity and Selectivity of Test methods
- Future testing
____
UNIT 4: Clinical Manifestations
Lecture 6: Lyme Disease – Signs, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
- Class Notes:
- Etiology and pathophysiology of Lyme disease.
- Clinical presentation stages.
____
UNIT 3: Chronic Conditions and Associations with Lyme Disease
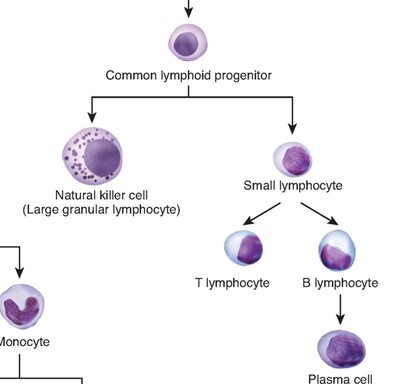
Lecture 7: Immune Implications
- Class Notes:
- Immune defenses against spirochetes & other tick-borne pathogens
- Immune escape mechanisms of spirochetes
- Immune suppression by spirochetes & other tick-borne pathogens
Lecture 8: Neurological Complications of Chronic Lyme/PTLDS
- Class Notes:
- Neurological manifestations of tick-borne diseases:
Severe headaches, Bell's Palsy, stiff neck, encephalopathy, visual disturbances, memory loss,
sleep disturbances, hearing loss, polyneuropathy, small fiber neuropathy,
- Immunological mechanisms leading to peripheral nerve damage. etc.
- Associations with autism
. Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)
- Possible association with tick-borne encephalitis virus (TBEV).
- Immunological mechanisms leading to peripheral nerve damage.
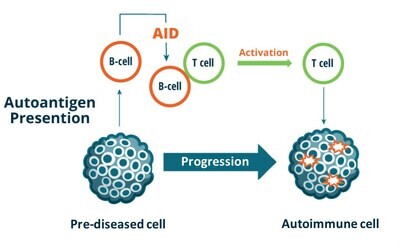
Lecture 9: Autoimmunity in Tick-borne Diseases
A. Introduction to Autoimmunity in Tick-borne Diseases
- Definition and concept of autoimmunity.
- Overview of how tick-borne infections can trigger autoimmune responses.
- Autoimmune Conditions and links to Tick-borne diseases: Lupus, Sjogren's Hashimoto's, MS, ALS, etc.
- Alpha gal Syndrome
D. Mechanisms of Autoimmunity and Chronic Illness
1. Inflammatory Response
- Cytokine production, inflammation, and tissue damage.
- Chronic inflammation and systemic effects.
- Factors predisposing to Chronic Illness risk: genetic, environmental and lifestyle.
E. Management and Treatment Strategies
1. Pharmacological Approaches
- Immune modulating drugs, steroids, specific treatments for autoimmune conditions.
- Management of chronic symptoms.
2. Lifestyle and Supportive Care
- Importance of patient education, counseling, and supportive therapies.
3. Challenges and Controversies
- Differences in medical opinions, guidelines, and practices.
F. Conclusion and Future Directions
- Recap of the complexity of autoimmune sequelae and chronic illness in tick-borne diseases.
- The need for more research and a multidisciplinary approach.
- Emphasizing patient-centered care and a holistic approach to management.
Recommended Readings:
- Various scientific articles and research studies relating to autoimmune reactions to tick-borne diseases (TBA)
- Clinical guidelines on diagnosing and managing autoimmune diseases associated with tick infections.
Lecture 10: Lyme Borreliosis & Arthritis
- Class Notes:
- Post-treatment Lyme disease syndrome.
- Neurological manifestations of tick-borne diseases.
- Management and rehabilitation.
- Clinical similarities and diagnostic confusion.
- Molecular mimicry between Borrelia antigens and host tissues.
- Treatment considerations.
Lecture 11: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS) and Tick-borne Diseases
- Class Notes:
- Possible associations and diagnostic challenges.
- Overlapping symptoms and differential diagnosis.
____
UNIT 5: Treatment, Prevention, and Future Challenges
Lecture 12: Pharmacological Approaches to Tick-borne Diseases
- Class Notes:
- Connection to other microbes: viruses, fungi and parasites
- Antibiotics, antiparasitics, and antiviral medications.
- Side effects and resistance issues.
- Addressing biofilm.
- Adjunctive therapies.
Lecture 13: Alternative Therapies
- Class Notes:
- Herbal Solutions
- Oxygen-based Antimicrobial Options
- Benefits of Fasting
- Frequency-based therapies
- Vagal Tone & Healing of Emotional Trauma
Lecture 14: Nutrition Implications
- Class Notes:
- Anti-inflammatory Diets
- Auto-Immune Diet
- Gut Healing
- Nutrient Deficiencies resulting from long-term infections
- Functional Medicine Nutrition for Lyme & Co
Lecture 15: Future Challenges and Closing Thoughts
- Class Notes:
- The evolving nature of tick-borne diseases.
- Predictions and areas of research.
- The importance of interdisciplinary approaches.