Genes and Vaccines
Genes and Vaccines
Genes and Vaccines
Fall 2025 (Sept-Dec)
Syllabus (Subject to Change)
Instructor: Dr. Kendra Becker
First class is Tuesdays, 2nd week of September at Noon, weekly noon thereafter
Description
Join us for an in-depth look at some of the most pivotal genes of the human body. Take a deep dive into disease risk, detoxification of toxins, healing components, gut health, and immune system health. This course will splice out several important genes and discuss their complexity in the body. Furthermore, continuing the discovery of how these genes work together and modulate other metabolic processes. The final weeks of this class will put all the learned information together for practical application on diet, lifestyle, and supplementation. MTHFR, MTR, COMT. DAO, MAO and more will be covered.
Topics
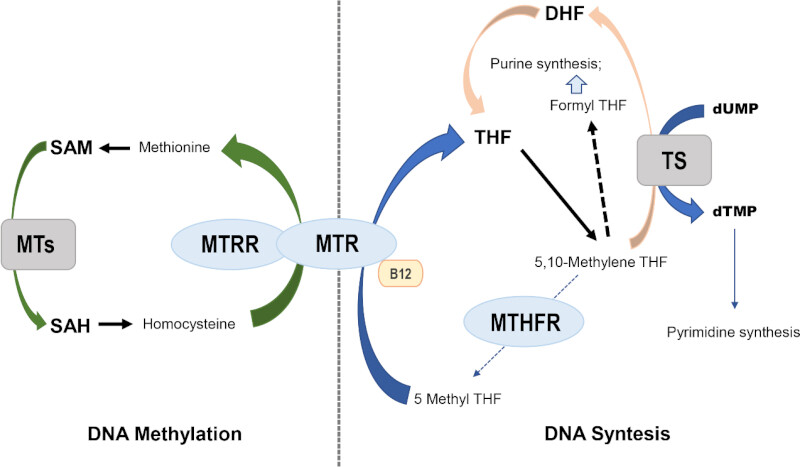
1-3. MTHFR- The MTHFR gene’s purpose is to produce the important MTHFR enzyme in the body. This enzyme is an important part of maintaining optimal health. If the MTHFR gene has a variant, folate metabolism can be negatively impacted. Improper folate metabolism is implicated in many different diseases.
4. MTR-MTR codes for the enzyme, methionine synthase (MS). MS converts homocysteine to methionine using methylated vitamin B12. variants in this gene significantly impact homocysteine metabolism, which can increase the risk for a number of chronic conditions such as cardiovascular diseases, metabolic and neurological conditions and certain cancers. 30
5. MTRR-The MTRR gene codes for the important enzyme, methionine synthase reductase (MSR). Methionine synthase reductase is required for the proper function of methionine synthase (see MTR). Both genes act together to convert homocysteine to methionine. variants can be involved with the development of cancers, Parkinson’s disease, depression, hypertension and many others. 31-36
6-7. COMT-COMT is the major gene involved in methylation. It plays an important role in a variety of disorders, including estrogen-induced cancers, Parkinson’s disease, depression, hypertension and many others. COMT is also necessary for maintaining the proper balance of neurotransmitters with SAMe obtained from methionine. Genetic variants in COMT can result in various neurological problems and has also been associated with Autism.
8. AHCY-AHCY is the only enzyme known to convert S-Adenosylhomocysteine (AdoHcy) to homocysteine. It is crucial that AHCY immediately converts AdoHcy to homocysteine and adenine in order to maintain optimal methylation potential. Studies show a link between variants in this gene with poor methylation potential and severe myopathies, developmental delays and hypermethioninemia.
9. b12 and Homocysteine- Homocysteine is an amino acid that is involved in maintaining the methionine cycle. Elevated homocysteine levels are well known risk factors for chronic disease, particularly cardiovascular, diabetes and neurodegenerative disorders. Homocysteine and folate metabolism is closely linked to DNA methylation and contribute substantially to preservation of DNA integrity. Consequently, genetic polymorphisms that influence homocysteine and folate metabolism are associated with different types of cancer including NHL, acute leukemias, and colorectal cancer. Also discussing Methionine synthase (MS) as an important enzyme in folate metabolism.
10. folate and its importance - Mitochondrial folate metabolism is a central player in the one carbon pathway, which is essential for nucleotide biosynthesis as well as methylation and reductive reactions. This is influenced by several processes, especially dietary intake and the polymorphisms of the associated genes involved. Aberrant folate metabolism therefore affects both methylation and the DNA synthesis processes. Proper use of folate is dependent on the availability of folate from the diet.
11. MTHFR & COMT putting it together- dopamine-related genes like COMT gene, which are involved in dopamine metabolism, and MTHFR gene, which may affect COMT methylation and COMT function. Both require b12 for proper function but Balancing the recommendations of methyl folate and B12 can at times be tricky.For example, giving more methylfolate and the body begins to produce more neurotransmitters the body will have a difficulty clearing them with a COMT gene mutation. Since the COMT is greatly affected by toxins and the environment if there is a further burden on this system, leading to adverse effects from methylfolate.
12.MAO & DAO, histamine and pregnancy- histamine is associated with many problems. However, it can be difficult to identify if it is a production, distribution or breakdown problem. Examining MAO and DAO and their roles part histamine plays in a variety of conditions.
13.Diet and Lifestyle Factors- navigating genetics and epigenetics can be challenging. This module will cover factors like nutritional choices to boost glutathione, minimize toxin overload and support overall mitochondrial health.
14. Supplementation- supplements can be amazingly helpful and also harmful. It is imperative to understand genetics before recommending or consuming any supplements. This module will cover how to dose supplements, proper ratios of supplements, and assessing need of supplements
15. Putting it all together- Genes, food, supplements, mitochondrial health and a review